Browse Items (8239 total)
Sort by:
-
"July 16th confirmed as definite for Apollo 11."
News article covering NASA's announcement of Apollo 11's launch-date: July 16th. -
"Five manned Apollo flights scheduled this year."
News article detailing the planning of five more projects after the successful mission of Apollo 8. -
"Countdown trials start for launch."
News article detailing how the crew of the Apollo 8 are preparing for launch with a "dry run." -
"Dec. 21 - 4:51 a.m. -One of great explorations of all time begins."
News article detailing how Apollo 8 is ready for launch and the anticipation surrounding it. -
"Astronaut trio sees 'successful' Apollo 9 mission."
News article detailing the hope from the Apollo 9 crew that their mission will be a success. -
"Moon brought near by Apollo 8 mission."
News article detailing the recovery of the Apollo 8 crew after its successful mission. -
"All systems 'go' for liftoff of Apollo 10."
News article detailing that the final preparations for the lift-off of the Apollo rocket have been completed. -
"Six-engine cluster of the Saturn S-IV rocket."
A press-release detailing the successfuly firing and the specfic launching information of the Saturn I-V rocket-launch. -
"The significance of parameters affecting the heat transfer to the liquid hydrogen in the Saturn S-IVB stage for the lunar orbit rendezvous mission."
The Saturn S-IVB stage has a requirement for orbiting around the earth for up to 4.5 hours with approximately 60 percent of its initial propellant remaining at the end of the coast (prior to restart) . Extensive analyses must be performed to insure that this requirement is met. Both the maximum and minimum heat transfer rates are important because the maximum rates affect the hydrogen boiloff losses and thus the initial propellant loading requirements. The minimum rates are important because the boil off gases are used to maintain a minimum axial thrust level by venting the gases continuously through aft facing nozzles. This provides for a settling of the propellant throughout the orbital coast and alleviates the need for periodically venting the tank under zero gravity. -
"Signal distribution in automatic checkout systems."
This paper deals with several selected aspects of the signal distribution in automatic checkout systems. These are: 1) The use of relay matrices as control elements; 2) The inclusion of self-checking capabilities; 3) Problems of systems integration. These aspects are not unique to automatic checkout systems. However, due to the nature of automatic checkout systems as presently being designed around digital circuitry, they find either fuller or different applications than in other types of systems. Also, while they are on the surface somewhat disconnected in nature, they tend to interrelate during the implementation of an automatic checkout system. -
"Sensitivity of rocket engine stability to propellant feed system dynamics."
Because of the increased reliability required of rocket systems in their more recently assigned missions, previously acceptable design features must be reappraised ad refined. In the region of rocket engine system stability, the probles is centered in two areas, the combustor and the propellant feed system The principal interest of this paper lies in the coupling that occurs between the feed system and combustion dynamics, often termed a "buzzing" instability then the dymics are characterized by periodic pressure oscillations in the range of 200 to 1000 cps appearing in the combustion chamber and' the feed system. -
"Selected methods for uprating Saturn vehicles."
This paper will discuss selected methods for increasing the Saturn launch vehicle payload capabilities. These methods involve system changes or additions that give large step performance'increases aver those which can be obtained by product improvements. The selected philosophy of approach and the established designed systems wil1,be described, as well as anticipatedsystem concepts that may be used to increase the Saturn vehicles' capabilities. -
"Statement of George E. Mueller, Associate Administrator for Manned Space Flight before the Committee on Aeronautical and Space Sciences, United States Senate."
Presentation of George Mueller before congress. Contains illustrations. -
"Standard procedure for using units of mass, weight, force, pressure and acceleration."
Report No. DT-TM-1-60. ; FORWARD: The field of missiles and rockets deals with quantities of matter at various locations with different accelerations of gravity. The weight of these masses changes with gravity and the measurements of liftoff weight, fuel weight, etc., result in different values, depending on whether mass or weight units are used. Pressure and thrust are independent of the acceleration of gravity, but the instruments for measuring these values are calibrated with standard masses, producing different weight forces and calibration curves at different locations. Most sections of ABMA and other agencies or companies use pounds or kilograms as units of mass, weight or force, and the influences of different accelerations of gravity are often disregarded or treated incorrectly. These discrepancies become increasingly unacceptable with larger missiles and greater distances between operation sites. Therefore, the following Standard Procedure has been prepared to insure consistent and uniform terms and units of mass, weight, force, pressure and acceleration. All sections and individuals concerned are urged to use these units andprocedures. This is signed by Dr. Wernher von Braun, Director Development Operations Division. -
"Standards of conduct for NASA employees."
NASA handbook which establishes what code of conduct is acceptable as a representative of the company and what behavior is not. -
"Stability analysis of Apollo - Saturn V propulsion and Structure feedback loop."
The propulsion and the structure of a space vehicle form a feedback loop through inertial coupling referred to as the pogo phenomenon and experienced with the Thor , Titan, and Apollo-Saturn V space vehicles. -
"A new telemetry technique."
A technique new to telemetry is discussed which promises to alleviate an enigma facing the telemetry engineer : How to adequately transmit the avalanche of vibration and other wideband data desired in the development phase of large missiles and launch vehicles. The data channels are stacked in the frequency spectrum as single sideband subcarriers which frequency modulate the RF carrier. The system design utilizes to advantage the statistical properties of vibration data to achieve maximum data transmission efficiency from the available RF carrier deviation. However, in contrast to proposed statistical predigestion techniques, the data is transmitted in raw form. -
"Sperry Rand monthly progress report for July, 1969."
The following pages contain reports for each of the individual contract appendices covering technical progress and accomplishments, related problems, and staffing progress. The report of manhours expended against each appendix by schedule order is being submitted as a part of the financial management report. -
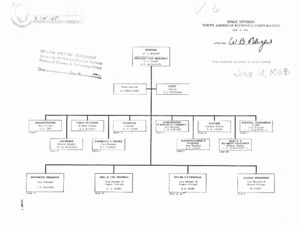
"Space Division, North American Rockwell Corporation Organizational Chart."
Organization chart for North American Rockwell, 1968 -
"Space vehicle test stands."
One of the pacing items in this Nation's accelerated space program is the construction of facilities for the manufacture, development, testing, check-out, transportation and launching of space vehicles. Behind each successful launching are countless hours of effort in development, quality and reliability checks and tests of engines, components, boosters, and stacked stages; including pressure tests, cold-flow tests and hot firing (or static) tests; all to assure the safest possible trip for the men or instrumentation in the space craft.