Browse Items (970 total)
Sort by:
-
"Draft Script for Saturn I/IB Quarterly Film Report No. 25 (Covering July, August, September, 1965)."
Draft script for quarterly report: July through September, 1965. -
"Dr. George Mueller: The Man Behind Manned."
G. E. Challenge. Article written about George Mueller, NASA Associate Administrator for Manned Space Flight. -
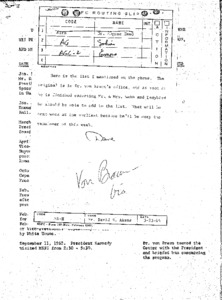
Dr. von Braun's calendars and scrapbooks indicate that these were his personal contacts with President Kennedy, Vice-President Johnson and members of their immediate staff.
The first page contains a typed routing slip. A list of Wernher von Braun's meetings with President Kennedy, the Vice President and members of their immediate staff. -
"Dr. von Braun/NASA HQ correspondence: July 1968."
This contains a two page list of the correspondence which is scanned separately. It includes the date and a brief description of the correspondence. -
Dr. von Braun's oral history interview transcript - Kennedy Library: memorandum.
This memorandum references the signed copies of Dr. von Braun's oral history interview for the John F. Kennedy Library. -
DX priority: memorandum.
Memorandum discussing the priorization of various nlunar landing vehicle projects. -
"Dynamic Environments of the S-IV and S-IVB Saturn Vehicles."
The vibration and acoustic environments of the S-IV and S-IVB Stages of the Saturn vehicle are summarized. A brief review of techniques used to predict the dynamic environments of the S-IV and S-IVB vehicles is presented. This review includes discussions on the prediction of rocket exhaust noise, boundary layer noise, sinusoidal vibrations, and random vibrations for the S-IV and S-IVB vehicles. In addition, sine-random vibration conversions are given. -
"Dynamic Loads of a Launch Vehicle Due to Inflight Winds."
Analysis of the stability and dynamic load environment of a launch vehicle resulting from atmospheric disturbances is a very complex problem. To determine the dynamic load environment of the vehicle requires an adequate description of the wind field, vehicle dynamics and control system. The essential of such a study, namely methods of analysis, wind field specification and representative vehicle response parameters for evaluation, are of equal importance. This paper is concerned with the mathematical foundations of the vehicle model and method of analysis. -
"Earth Orbital Workshop Capabilities Brochure."
A brochure designed to depict a competence and capability in the area of large earth-orbital workshops. -
"Effects of High-Pressure Hydrogen on Steels."
Hydrogen embrittlement of steels is hardly a new subject, but the effects of high-pressure hydrogen have been treated in detail only more recently and to a much more limited extent. Thus, most investigations of hydrogen embrittlement have been concerned with hydrogen in metals, while for the high-pressure hydrogen problem, we are more concerned with metals in(in contact with) hydrogen. I believe there is a difference and, certainly,different mechanisms of embrittlement are at least possible.; Presented at the Central Florid Section, American Welding Society, Orlando, Florida, 14 November 1967 and North Alabama Chapter, American Society for Metals, Huntsville, Alabama, 16 November 1967. -
"Saturn Vehicle Cryogenic Programs."
Paper from the 1965 Cryogenic Engineering Conference at Rice University, Houston, Texas, paper K-4. The abstract states, "This paper covers the cryogenic propellant and gaseous application to the George C. Marshall Space Flight Center Saturn Programs. Emphasis is placed on the overall application and the resultant logistic considerations. The planning of facilities, storage, and transportation required to ensure an adequate supply of cryogenic fluids when needed is traced from the engine and stage requirements. The entire cycle of technical requirements, estimating the quantities required from production and management of the program is developed, spacecraft application and other trends that affect cryogenic production are reviewed." -
"Design Concepts of Ground DDAS in Saturn 1B/V ESE."
In the Saturn IB/V programs the sheer quantity of data required for computer processing and ESE display makes it necessary to provide an efficient data acquisition system. For much of the data originating in the launcher this requirement is satisfied by the Ground Digital Data Acquisition System (DDAS). This paper provides a technical description of the Ground DDAS with emphasis placed on the unique design concepts of this telemetry system. -
"A Description of the ST 124-M Inertial Stabilized Platform and its Application to the Saturn V Launch Vehicle."
This report is a description of the ST124-M inertial stabilized platform system and its application to the Saturn V launch vehicle. It is a summary report providing the system concept and not a theoretical presentation. Mathematical equations were included only where necessary to describe the equipment; however, the detail derivations supporting these equations were not presented since this was not the theme of the paper. -
"Design, Development, and Fabrication of a Prototype Hydraulic Transformer."
For presentation to the Society of Automotive Engineers, 16 September 1964, Boston, Massachusetts. ABSTRACT: This paper discusses the design, development and fabrication of a prototype hydraulic transformer, Hydro-Aire Model No. 05-055, performed in fulfillment of the requirements of Contract No. NAS 8-5264 for NASA Marshall Space Flight Center. The Hydraulic Transformer described is designed to pump hydraulic oil at a flow of 100 GPM with a pressure rise of 4000 psi, and does this work by utilizing as a power source the flow of RP-1 rocket fuel at a pressure of 1900 psig. The Hydraulic Transformer built to handle this combination of flows and pressures, unprecedented in such devices, has a weight of only 70 pounds for the first development model. The development of this unit is discussed and future development improvements are mentioned. -
"Design and Development of a Zero-G Vapor Liquid Separator For Use in Cryogenic Fluid Power Systems."
During long coast periods of zero-gravity, storage vessels for the cryogenic liquids proposed for use in some power transmission systems undergo random distribution of the liquid and vapor phases therein. Thus, when heat flow into the vessel causes the vessel pressure to build-up requiring venting to maintain a safe value, the likelihood of venting the valuable liquid phase, as well as the vapor, results. To preclude this eventuality, various devices for separating the liquid and vapor phases and venting just the vapor have been studied and carried into the experimentation stages. -
"Design and Development of a 1,500,000-Pound-Thrust Space Booster Engine."
Describes the F-1 engine design and components. -
"Design of the Saturn S-IV Stage Propellant Utilization System."
Describes the SIV vehicle and its components. Presented at: IRE International Convention. -
"Design and Use of Fault Simulation for Saturn Computer Design."
Describes different aspect of the Fault Simulation for Saturn computer design. -
"Development and Utilization of Computer and Test Programs for Checkout of Space Vehicles."
A computer system was designed to allow test engineers to progressively employ automation in the checkout of the Uprated Saturn I and Saturn V space vehicle programs and still allow manual control of the checkout process. A two-computer system was selected by National Aeronautics and Space Administration, and the International Business Machines Corporation was chosen to provide the programming engineering necessary to implement these objectives. Space vehicle checkout, prior to launch, may be characterized by controlling, monitoring, and testing the vehicle and its subsystems through the use of ground support equipment (GSE).; IBM Huntsville Library.; Presented at AIAA Conference, XVIIth International Astronautical Congress, Madrid, Spain, October 10-15, 1966 by Edward A. Robin, Manager, Vehicle Test Programming Department. -
"Development Effort to Achieve Reliability."
Presented at the 6th West Coast Reliability Symposium, University of California at Los Angeles, Los Angeles, California, 20 February 1965.The development of a large liquid rocket engine can represent the expenditure of several hundred million dollars of effort. Before 30 percent of the contracted development funds have been expended, however, the engine will probably have operated for the mission duration. The capability to operate at least one successful test early in a development program is evidence of achieving a minimal reliability level, but the major objective of the development program is producing a design which performs reliably. A rocket engine reliability prediction must view reliability as a dynamic concept, constantly being altered by development effort.